EDGE COMPUTING - Cost Effective
Can you save cost By deploying edge computing ? YES !
There are several IT trends driving the need to reduce telecommunications latency and bandwidth costs, including internet of things (IoT) and content distribution networks (CDN). In comparison with the cloud or other remote data centers, “micro” data centers are located closer to the points of utilization, thereby reducing latency and costs. As well as providing physical infrastructure benefits, this distributed data center architecture is applicable to any small data center regardless of latency requirements.
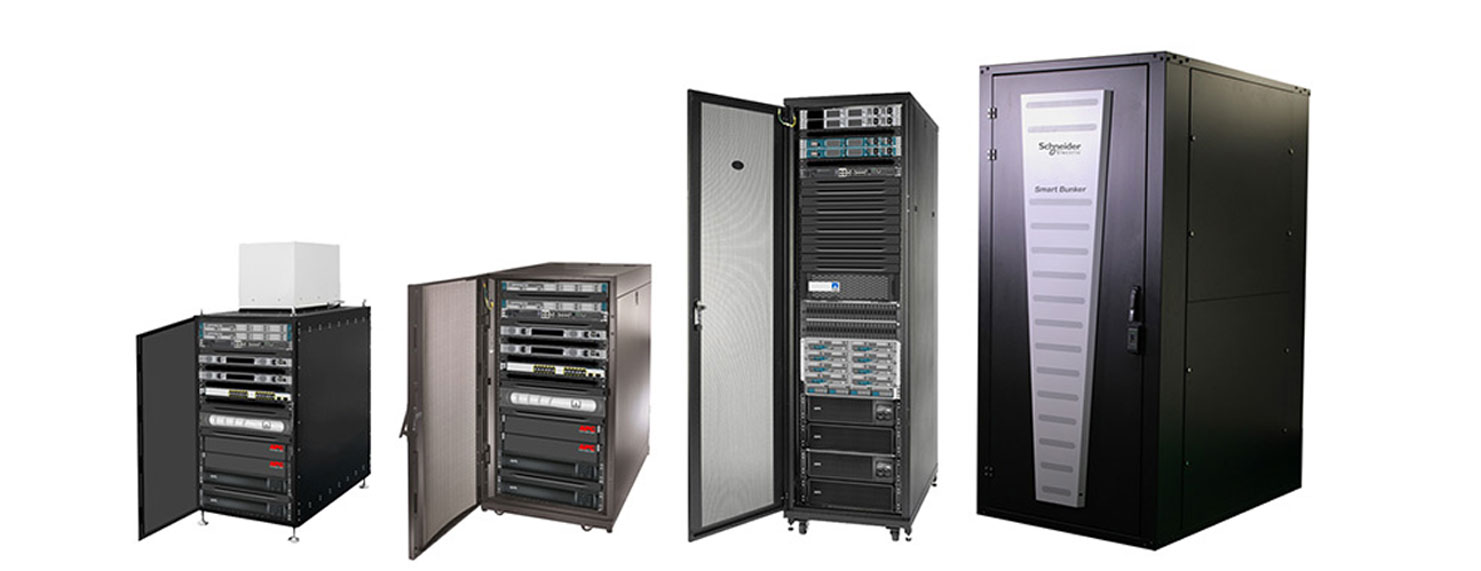

A self-contained, secure computing environment with all the necessary networking, processing, and storage for running applications is known as a single-rack micro data center2 (Figure 1). They arrive complete with all required power, cooling, security, and related management tools (DCIM) in a single enclosure. Micro data centres are put together and tested in a manufacturing setting. “Drivers” inspire or trigger an action. When compared to other options like server rooms and regular data centres, the adoption of micro data centres to support edge computing applications is primarily driven by the following four factors.
- Scalability
- Rapid deployment
- Dependability
- Cloud outsourcing, and colocation
Capital cost advantages:
The ability to typically run off of a building’s existing physical infrastructure is the major capital expense advantage that micro data centres have over developing a traditional centralised data centre. A mini data centre can frequently be supported by an existing structure using both utility and backup generator power. In other words, micro data centres are less capital-demanding than creating a new data centre because they can use the “sunk costs” in the facility’s electricity (such as switchgear), cooling (such as chillers), and core and shell construction.
Assumptions for traditional vs micro data center capex analyses | ||
| Cost component | Traditional data center | Micro data center |
| Rack density and quantity | 200 racks at 5 kWrack | 200 micro data centers at 5 KW/rack |
| Power & cooling redundancy | IN | IN |
| DX CRAC coding unit | Perimeter with condenser | Row-based with condenser |
| Containment type | Hot aisle | Ful (front & rear) |
| Core and shell cost | $1615 ($150) | $0 |
| Total UPS capacity (with monitoring) | 12 MW capacity double conversion online | 16MW capacity double conversion online |
| Environmental & Security | Yes | Yes |
| Fire suppression | Pre-action sprinkler | NOVEC1230 canister |
Findings
The capital expense for building a single centralized data center rated for 1MW of IT load is $6.98 million or $6.98/watt. The capital expense of 200 5kW micro data centers is $4.05 million or $4.05/watt. Micro data centers represent a 42% savings over a centralized data center. Note that if fire suppression was removed from traditional and micro data centers the overall savings would increase to 48% savings. This is because the pre-action sprinkler system cost in the traditional data center is significantly less than the NOVEC clean agent system assumed in the micro data center.
Methods of deployment
There are three basic ways you can deploy small data centers: 1. Build it from scratch by specifying, buying, and assembling individual parts , 2. Build it with a preconfigured solution and assemble the parts 3. Build it using a micro data center which comes prefabricated and fully as- sembled
We are one click away for a solid step forward.
Utilise our consulting service for energy efficiency and sustainability to monitor and improve your data centre.
Our Latest Project
Ac quisque ad tempor tincidunt nec dui. Sapien maecenas dui massa eros nullam. Aliquet fringilla blandit et facilisi eros molestie. Augue molestie pretium torquent sagittis pellentesque. Conubia facilisi tristique amet mattis potenti viverra orci. Iaculis curabitur ultrices accumsan duis lacinia. Nunc ac id pretium urna integer dui cubilia felis fames libero. Nisl faucibus tristique blandit nascetur laoreet curabitur ante per fermentum.