In an era where digital operations are the backbone of nearly every industry, the significance of Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems has never been more pronounced. These systems are not just backup plans; they are foundational elements that ensure resilience, reliability, and continuity in modern infrastructure.
Imagine a scenario where critical operations are halted due to a power outage—data is lost, equipment is damaged, and productivity is stalled. UPS systems prevent such scenarios by providing emergency power during outages, ensuring that essential functions continue seamlessly.
These silent guardians of modern infrastructure, from data centers to hospitals, stand at the ready, ensuring that when power fluctuations or outages strike, the heartbeat of our modern infrastructure doesn’t skip a beat.
This blog explores the indispensable role of UPS systems, their various applications, and how they fortify critical infrastructure against the unexpected.
What is a UPS?
An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) is a power protection device that delivers a continuous supply of electric power to critical systems with two main functions:
- It is an emergency power system that provides a backup energy source during utility power failures. Depending on the outage duration, a UPS can keep a system running long enough until utilities or generators come online, or it can provide enough time to shut down the system properly and avoid data loss.
- It protects against power surges and sags that could damage sensitive electronic hardware.
The Role of UPS in Critical Infrastructure
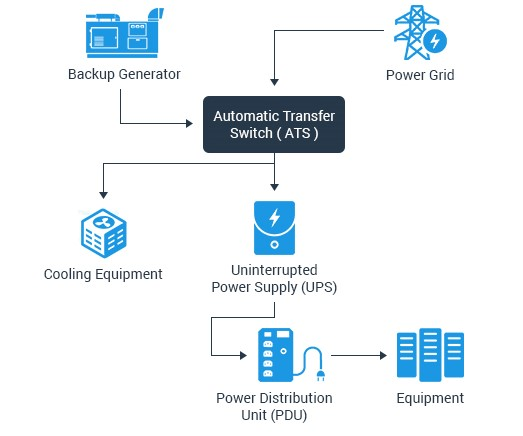
At the core of critical facilities like hospitals, data centers, and financial institutions, UPS systems serve as the first line of defense against power-related disruptions. They ensure that life-saving equipment, crucial data processing units, and financial transactions continue uninterrupted, thereby maintaining the operational integrity of essential services.
Various Roles of UPS
- Data Protection: UPS systems prevent data loss during sudden power outages by providing enough backup power for systems to shut down properly.
- Equipment Safety: They shield sensitive electronics from power surges, spikes, and voltage drops, prolonging equipment lifespan.
- Operational Continuity: In industries where every second counts, UPS systems ensure that operations proceed without interruption, maintaining productivity and service delivery.
- Emergency Power: UPS systems provide immediate backup power during outages, ensuring essential services remain operational.
Benefits of UPS
The advantages of implementing UPS systems extend beyond mere power backup. They include:
- Reliability: UPS systems offer peace of mind, knowing that the power supply will remain stable regardless of external conditions.
- Cost Efficiency: By preventing equipment damage and data loss, UPS systems save businesses from potentially enormous recovery costs.
- Scalability: Modern UPS solutions can be scaled to meet growing power demands, making them a long-term investment in operational stability.
- Equipment Protection: Safeguarding sensitive equipment from damaging power fluctuations.
- Data Integrity: Preventing data loss during unexpected power disruptions.
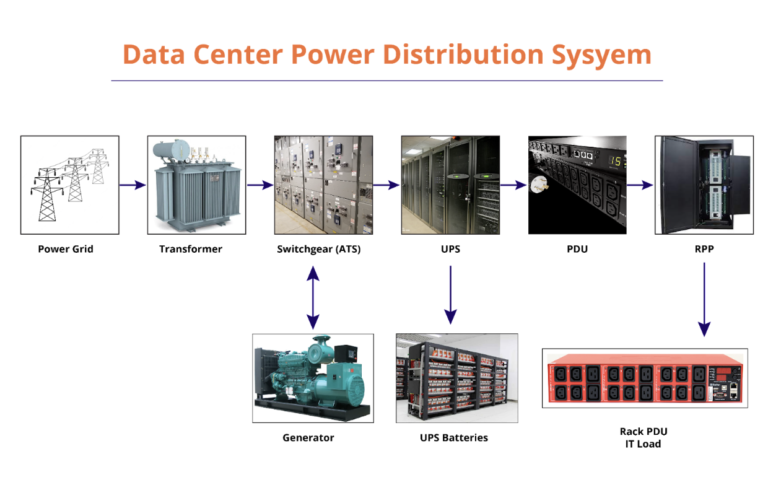
How UPS Works
At the heart of a UPS system lies its ability to instantly switch to battery power when it detects a power failure, providing a seamless transition that keeps connected devices running.
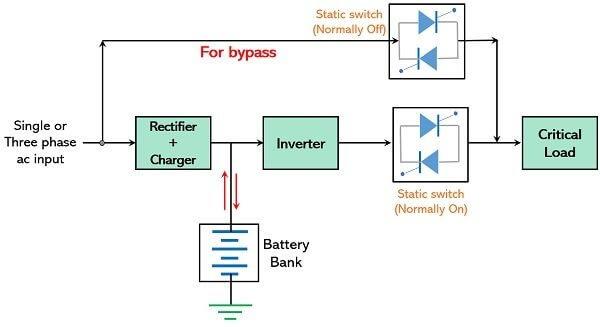
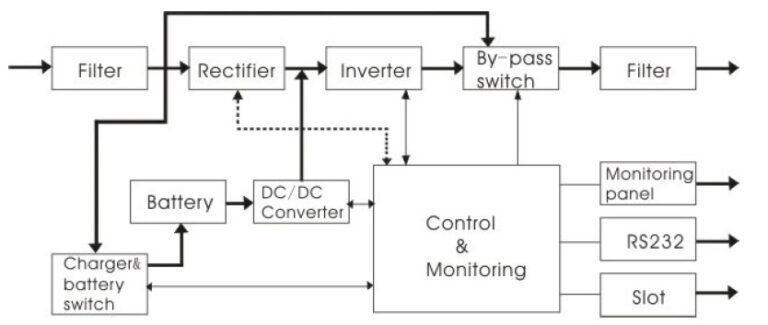
The system typically comprises a rectifier, battery, inverter, and a static switch, working together to ensure uninterrupted power.
The rectifier converts incoming AC power to DC to charge the battery, while the inverter does the reverse, ensuring a steady AC supply during outages. Advanced UPS systems also include a bypass circuit for maintenance and a surge protection component to handle sudden voltage spikes.
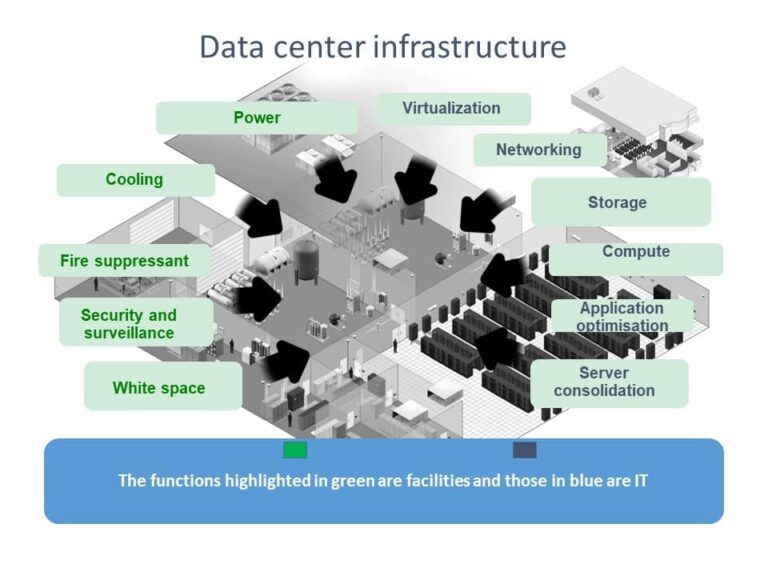
At a Large Scale, such as at Data Centers
In data centers, UPS systems are critical for maintaining 24/7 operations. They not only provide backup power but also ensure the quality of power feeding into servers and networking equipment, preventing data loss and hardware damage due to power issues.
They provide clean, stable power to protect servers and networking equipment, ensuring data integrity and availability. The scale of UPS deployment in data centers is vast, often involving redundant systems to guarantee uptime even during maintenance or component failure.
Types of UPS Systems and Their Applications
UPS systems come in various forms, each suited to different needs:
- Standby UPS: Ideal for small office and home use, providing basic protection against power outages.
- Line-Interactive UPS: Used in small to medium businesses, offering enhanced voltage regulation.
- Online UPS: The most robust form, providing continuous power conditioning and is essential for critical applications like data centers and hospitals, offering the highest level of protection by continuously filtering power.
Online Double Conversion UPS:
- Constant Power Flow: Power continually flows through the UPS, from AC to DC for battery charging, and back to AC for the load.
- Isolation from Irregularities: Provides complete isolation from power irregularities on the main supply.
- High-Quality Power Output: Delivers a perfect sine wave, ensuring high-quality power free from disturbances like harmonics and waveform distortion.
- Zero Transfer Time: Offers continuous, high-quality power with no break when switching to battery, ensuring seamless operation.
- Ideal for Critical Loads: Best suited for protecting large data centers and sensitive equipment due to its ability to provide the highest level of power quality consistently.
- Frequency Regulation: Provides frequency regulation, crucial when paired with backup generators.
Line-Interactive UPS:
- Voltage Regulation: Offers voltage regulation by boosting or reducing power without switching to battery, making it effective against power fluctuations.
- Moderate Protection: Provides a balance between protection and operating costs, suitable for areas with fewer outages but common fluctuations.
- Battery Use: Uses the battery to condition power, leading to more frequent battery use compared to online UPS systems.
- Inverter Always On: The inverter is always part of the output, ensuring additional filtering and reduced switching transients compared to standby UPS.
- Typical Use: Commonly used in smaller rackmount applications under 5000VA.
Offline/Standby/Battery Backup UPS:
- Cost-Effective: A budget-friendly option offering basic protection against power spikes and short outages.
- Direct Power Pass-Through: Passes utility power directly to the output, switching to battery power during outages.
- Transfer Time: Features a 6-8 millisecond break in power when switching to battery backup, generally acceptable for less critical applications.
- Best Suited For: Ideal for lower capacity needs such as small offices, personal computers, and non-essential electronics.
- Surge Protection: Provides basic surge protection, enhancing the safety of connected devices during power spikes.
How These Various UPS Systems Work
Standby UPS systems wait idly until a power disruption occurs, then switch to battery power.
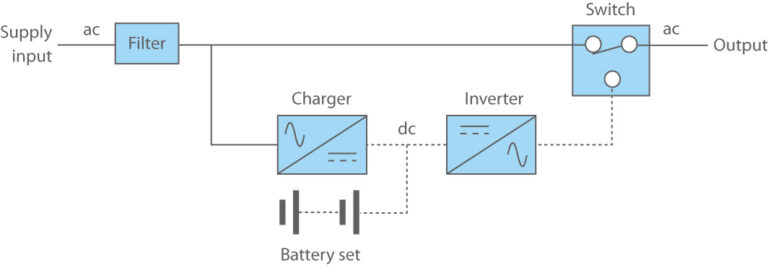
Offline UPS, also called standby UPS or battery backup. When an input power failure happens, the built-in battery and the inverter, which converts the battery’s DC power to AC, are activated and connected to the output by the transfer switch. There is generally about a 6-8 millisecond break in power when transferring to battery backup.
Line-interactive UPS systems adjust voltage levels continuously, using the battery sparingly.
With line-interactive UPS, the inverter becomes part of the output and is always on. The inverter can operate in reverse to charge the battery while AC input is normal, and switch to battery power when input fails, which provides filtering and voltage regulation. When AC input power fails, the unit’s transfer switch opens and the power flows from the battery to the UPS output. With the inverter always on and connected to the output, line-interactive UPS provides additional filtering and yields reduced switching transients when compared to a standby UPS. Line-interactive UPS systems are typically used in rackmount applications below 5000VA.
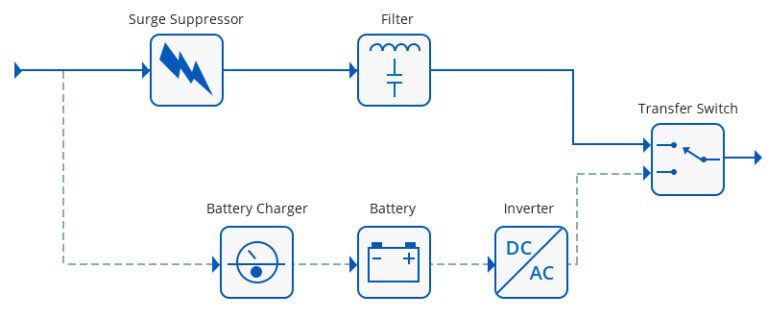
Double-conversion UPS systems also known as “online” UPSs, convert power twice which constantly converts power from AC to DC (and back), providing a steady and clean power supply.
The online UPS takes the incoming AC power supply and converts it to DC using a rectifier to feed the battery and the connected load via the inverter so that no power transfer switches are necessary. If the main AC input fails, the rectifier drops out of the circuit and the batteries keep the power flowing to the device connected to the UPS. When AC input power is restored, the rectifier resumes carrying most of the load and begins charging the batteries.
Choosing the Right UPS for Your Data Center
Selecting the appropriate UPS involves assessing your power needs, understanding the criticality of your operations, and considering future expansion plans. It’s crucial to balance cost with the level of protection required, ensuring that your data center remains resilient against power disturbances.
It is important to consider future growth, ensuring the UPS system can adapt to evolving power demands. Consulting with experts like P&C can provide tailored solutions that align with specific operational needs.
P&C’s Approach to UPS Solutions
At P&C, we specialize in tailoring UPS solutions to meet the unique needs of our clients. From initial consultation to installation and maintenance, our approach is holistic and involves a comprehensive assessment of your current and future power requirements, ensuring that the UPS system not only meets but exceeds your expectations for reliability and performance.
Maintaining and Upgrading Your UPS Systems
Regular maintenance is key to the longevity and reliability of your UPS system. P&C offers scheduled maintenance services, ensuring that your system is always in top condition. Moreover, we provide guidance on when and how to upgrade your UPS to keep pace with your growing power needs.
Client Success Stories in the UAE
Our portfolio in the UAE includes successful UPS installations across various sectors, from large data centers to healthcare facilities. These stories highlight the critical role of UPS systems in ensuring operational continuity and the trust our clients place in P&C’s expertise.What the Future Holds and New Inventions Worth Exploring
The future of UPS technology is geared towards higher efficiency, sustainability, and smarter systems. Innovations like lithium-ion batteries, modular designs, and IoT integration for real-time monitoring are shaping the next generation of UPS solutions. These advancements promise enhanced reliability, longer lifespans, and improved energy efficiency.